In the ever-evolving landscape of digital communication, the ability to decipher and understand the sentiments expressed in text has become paramount. Sentiment analysis tools, ranging from advanced machine learning models to user-friendly online platforms, have emerged as indispensable assets for individuals and businesses alike. This article delves into the realm of sentiment analysis tools, exploring their diversity, applications, and the evolving techniques that drive this transformative field.
What Tool is Used for Sentiment Analysis?
Choosing the right tool for sentiment analysis is pivotal for accurate and insightful results. Various tools cater to different needs, from comprehensive machine learning models to more accessible online platforms. Renowned sentiment analysis tools like VADER (Valence Aware Dictionary and Sentiment Reasoner), TextBlob, and IBM Watson Natural Language Understanding stand out for their effectiveness in categorizing sentiments as positive, negative, or neutral. As Maya Angelou once said, “Words mean more than what is set down on paper. It takes the human voice to infuse them with deeper meaning.” These tools act as digital interpreters of the human voice, unraveling the intricacies of emotions embedded in textual data.

How to Use ChatGPT for Sentiment Analysis?
ChatGPT, developed by OpenAI, has revolutionized natural language processing and understanding. While not explicitly designed for sentiment analysis, ChatGPT can be harnessed for this purpose. By crafting queries that prompt the model to evaluate sentiments or opinions, users can glean insights from its responses. However, it’s essential to note that ChatGPT’s primary strength lies in generating human-like text rather than sentiment analysis. As with any tool, it’s crucial to tailor its use to the specific requirements of the task at hand, as Albert Einstein aptly noted, “The formulation of the problem is often more essential than its solution.”
What Are the Techniques Used in Sentiment Analysis?
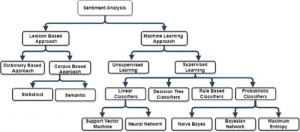
Sentiment analysis employs a spectrum of techniques, from traditional rule-based approaches to sophisticated machine-learning algorithms. Rule-based methods rely on predefined linguistic rules and lexicons, assigning sentiments based on the presence of positive or negative words. Machine learning models, including Support Vector Machines (SVM), Naive Bayes, and deep learning techniques like recurrent neural networks (RNNs) and transformers, excel at learning patterns and context from large datasets. These techniques enable a more nuanced understanding of sentiments, transcending the limitations of rule-based systems.
Which OpenAI Model is Best for Sentiment Analysis?
OpenAI has introduced several powerful language models, with GPT-3 being one of the most advanced. While GPT-3 is a versatile model for natural language understanding, its application to sentiment analysis might require task-specific fine-tuning. The choice of the best OpenAI model depends on the specific requirements of the sentiment analysis task at hand. As technology continues to advance, OpenAI’s models are poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of sentiment analysis and language understanding.
Sentiment Analysis Tools Online
The digital age has ushered in a wave of sentiment analysis tools available online, catering to diverse needs and skill levels. Online platforms like commentsanalytics.com, MonkeyLearn, RapidMiner, and Aylien offer user-friendly interfaces for sentiment analysis, democratizing access to this powerful technology. These tools serve as virtual interpreters, enabling users to analyze sentiments in textual data without the need for extensive programming knowledge. As Steve Jobs envisioned, “The most powerful person in the world is the storyteller.” Online sentiment analysis tools empower individuals to tell their stories with a deeper understanding of the emotions woven into their narratives.
Sentiment Analysis Tool Online Free
For those seeking cost-effective solutions, several sentiment analysis tools are available online for free. TextBlob, for instance, is a Python library that provides a simple API for common natural language processing (NLP) tasks, including sentiment analysis. Leveraging free online tools allows users to explore the capabilities of sentiment analysis without financial barriers, democratizing access to this transformative technology. In the spirit of collaboration, these tools offer a gateway for individuals and small businesses to harness the power of sentiment analysis.
Stock Market Sentiment Analysis Tools
Sentiment analysis transcends the realms of social media and customer reviews, extending its influence to the dynamic arena of stock markets. Tools like RavenPack and Accern specialize in analyzing sentiments expressed in financial news and social media to gauge market sentiment. In the words of Warren Buffett, “The stock market is designed to transfer money from the active to the patient.” Sentiment analysis tools in the stock market domain empower investors with timely insights, enabling them to make more informed and patient decisions in the ever-fluctuating financial landscape.
Sentiment Analysis Tools Python
Python, with its rich ecosystem of libraries, has become a go-to language for sentiment analysis implementations. Libraries like NLTK, spaCy, and scikit-learn provide robust NLP capabilities, making sentiment analysis more accessible to Python developers. The simplicity and readability of Python, coupled with the flexibility of these libraries, empower developers to seamlessly integrate sentiment analysis into their applications. As Python enthusiasts often proclaim, “Readability counts,” and sentiment analysis tools in Python embody this ethos, facilitating the creation of clear and effective code.

In conclusion, the world of sentiment analysis tools is a diverse and dynamic landscape, offering a spectrum of solutions for individuals and businesses alike. From established models and online platforms to Python libraries and specialized tools for stock market analysis, the choices are abundant. As sentiment analysis continues to evolve, these tools act as catalysts, amplifying our ability to comprehend the rich tapestry of human emotions encoded in textual data. In the words of Carl Jung, “The meeting of two personalities is like the contact of two chemical substances: if there is any reaction, both are transformed.” Similarly, the synergy between human intuition and sentiment analysis tools transforms our understanding of language and emotions in the digital age.