In a world where data drives decision-making, qualitative and open-ended questions have emerged as indispensable tools for uncovering nuanced insights that quantitative data alone cannot provide. Whether in research, counseling, or business, these questions play a pivotal role in unraveling the complexities of human behavior, thoughts, and emotions. This article delves deep into the realm of qualitative and open-ended questions, exploring their significance, applications, and techniques for effective implementation.
Open-Ended vs. Closed-Ended Questions
Unlocking the Power of Open-Ended Questions
At the heart of any meaningful conversation or research inquiry lies the choice between open-ended and closed-ended questions. Closed-ended questions, which can be answered with a simple “yes” or “no” or by selecting from predefined options, offer efficiency and ease of analysis. However, when the goal is to delve into the depths of human experience and gain rich, contextual insights, open-ended questions reign supreme.
“Questions are the keys that cause the secret doors of the psyche to swing open.” — Clarissa Pinkola Estés
Open-ended questions invite individuals to share their thoughts, feelings, and opinions in their own words. They allow for unfiltered responses, fostering a more profound understanding of a person’s perspective. For instance, if you ask, “Did you enjoy the event?” a closed-ended question, you may receive a simple “yes” or “no.” However, an open-ended version, such as “What were your thoughts and feelings about the event?” invites a more comprehensive and personal response.

Closed-Ended Questions: The Limitation of Choice
Closed-ended questions, while useful in specific scenarios, inherently limit the scope of responses. They are often employed in surveys, quizzes, and multiple-choice exams, where efficiency and standardized data collection are paramount. However, they lack the depth and breadth that open-ended questions offer.
Consider a customer satisfaction survey that asks respondents to rate a product on a scale of 1 to 5. While this yields quantifiable data, it fails to capture the specific reasons behind a low rating. Was it the product’s quality, functionality, or customer service that disappointed the customer? Only open-ended questions can provide the necessary context.
Open-Ended Responses
Unearthing Depth in Responses
Open-ended responses provide a canvas for individuals to express themselves freely. They encourage participants to share their unique perspectives, stories, and emotions. These responses often reveal unexpected insights, transforming raw data into a treasure trove of information.
“Answers are closed rooms; and questions are open doors that invite us in.” — Nancy Willard
In various fields, such as market research and therapy, open-ended responses are crucial for understanding the “why” behind actions, decisions, and emotions. When someone shares their experiences and reasoning in their own words, it can lead to profound revelations.
For example, consider a patient in therapy responding to the question, “How has your recent life event affected you?” An open-ended response might uncover deep-seated emotions and thought patterns, providing the therapist with valuable insights to guide the therapeutic process.
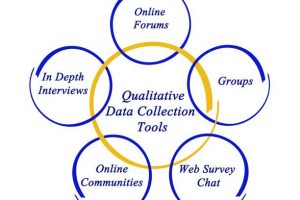
Qualitative Feedback
Nurturing Insightful Feedback
Qualitative feedback is a potent source of information for organizations, educators, and professionals seeking to improve their products, services, or interactions. Unlike quantitative feedback, which relies on numerical ratings, qualitative feedback delves into the specifics of what went well or poorly.
“Feedback is the breakfast of champions.” — Ken Blanchard
Whether collected through surveys, interviews, or comment boxes, qualitative feedback offers a more comprehensive understanding of user experiences. It captures the nuances, pain points, and suggestions that quantitative data may overlook.
For instance, when a restaurant solicits qualitative feedback from diners, it can gain valuable insights into the overall dining experience. Comments about the ambiance, food quality, service, and specific dish preferences allow the establishment to make informed improvements.
Qualitative Text Analysis
Unveiling Insights through Textual Exploration
Qualitative text analysis is the process of examining open-ended responses, comments, or written narratives to extract meaningful patterns, themes, and insights. This analysis method requires a keen eye for detail, as it involves interpreting the richness of language and context within textual data.
“Words are the source of misunderstandings.” — Antoine de Saint-Exupéry
When dealing with large volumes of text, qualitative text analysis becomes an invaluable tool. Researchers, marketers, and psychologists use it to make sense of the vast array of unstructured data generated through surveys, interviews, and social media.
For example, a social scientist studying public sentiment about a controversial political issue might employ qualitative text analysis to uncover the prevailing themes, emotions, and opinions within thousands of tweets and Facebook posts.

Analysis of Text Example
Peering into the Analytical Process
Let’s delve into a practical example of how qualitative text analysis can unlock insights. Imagine a company conducting customer surveys after a product launch. One of the open-ended questions posed to customers is, “What do you like most about our product?” Through qualitative text analysis, the company can discern several key themes:
- Product Features: Many customers praise specific features of the product, such as its user-friendly interface and innovative design.
- Customer Support: Some customers express gratitude for the exceptional customer support they received when facing issues.
- Value for Money: Several responses highlight the product’s affordability and the perceived value it offers.
- Ease of Use: Many respondents appreciate how easy it is to use the product, making it accessible to a wide range of users.
- Versatility: A few customers mention how the product caters to their diverse needs and preferences.
This analysis provides the company with valuable insights into the aspects of their product that resonate most with customers. Armed with this information, they can make informed decisions about marketing strategies, product enhancements, and customer support improvements.
Effective Open-Ended Questions
Crafting Questions That Elicit Rich Responses
The art of crafting effective open-ended questions lies in the ability to prompt thoughtful, detailed, and honest responses. When done correctly, these questions can unlock valuable insights that drive decision-making and problem-solving.
“Successful people ask better questions, and as a result, they get better answers.” — Tony Robbins
Here are some strategies for creating effective open-ended questions:
- Start with “How” or “What”: Begin questions with “How” or “What” to encourage respondents to provide detailed responses. For example, instead of asking, “Did you enjoy the event?” ask, “What aspects of the event did you find enjoyable, and why?”
- Avoid Leading Questions: Ensure that questions are neutral and do not lead respondents toward a particular response. Leading questions can bias the results.
- Use Follow-Up Questions: If a respondent provides a brief answer, use follow-up questions to dig deeper. For instance, if someone mentions they love a product, ask, “Can you tell us more about what specifically you love about it?”
- Allow Silence: Give respondents time to think and respond. Silence can prompt individuals to share more thoughtful answers.
- Balance Open-Ended and Closed-Ended Questions: Use a mix of open-ended and closed-ended questions to collect both qualitative depth and quantitative data.
Effective open-ended questions serve as the gateway to valuable insights, enabling businesses and researchers to make data-driven decisions.
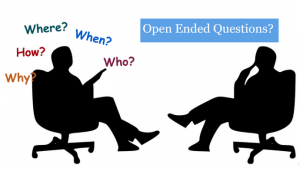
Open-Ended Questions in Research
Uncovering Hidden Dimensions in Research
In the realm of research, open-ended questions are instrumental in exploring the complexities of human behavior, attitudes, and motivations. They provide a holistic view of a subject, complementing quantitative data with qualitative richness.
“Research is to see what everybody else has seen and to think what nobody else has thought.” — Albert Szent-Györgyi
Here are some scenarios where open-ended questions shine in research:
- Exploratory Research: When entering uncharted territory, open-ended questions allow researchers to collect foundational insights and generate hypotheses.
- Qualitative Research: In-depth interviews and focus groups often rely heavily on open-ended questions to explore participants’ experiences and perspectives.
- Mixed-Methods Research: Combining open-ended and closed-ended questions enables researchers to triangulate data and gain a comprehensive understanding of a subject.
- Content Analysis: Researchers use open-ended responses for content analysis, identifying themes and patterns within textual data.
For instance, a sociologist studying the impact of technology on social interactions might conduct open-ended interviews with individuals to uncover the subtleties of their experiences and challenges in maintaining meaningful relationships in the digital age.
Open-Ended Questions in Counseling
Building Trust and Insight in Counseling
In the field of counseling and therapy, open-ended questions serve as powerful tools for building rapport with clients and gaining a deeper understanding of their emotions, thoughts, and experiences.
Counselors and therapists use open-ended questions to:
- Elicit Emotions: Questions like, “How are you feeling today?” invite clients to express their emotions openly, setting the stage for therapeutic discussions.
- Explore Trauma: Open-ended questions help therapists explore the origins and impact of traumatic experiences in a client’s life.
- Promote Reflection: Questions that encourage self-reflection, such as “What do you think is causing these feelings?” facilitate personal insight.
- Identify Goals: By asking open-ended questions about what clients hope to achieve in therapy, counselors can tailor treatment plans accordingly.
In a counseling session, the skillful use of open-ended questions can create a safe space for clients to explore their feelings and experiences, ultimately leading to personal growth and healing.

In-Depth Interview Software
Leveraging Technology for Deeper Insights
In today’s digital age, technology has revolutionized the way researchers and organizations collect and analyze qualitative data. In-depth interview software has emerged as a valuable tool for conducting structured interviews, managing data, and uncovering meaningful insights.
“Technology empowers people to do what they want to do. It lets people be creative.” — Steve Ballmer
Key features of in-depth interview software include:
- Questionnaire Design: Software allows researchers to design and customize questionnaires, ensuring that open-ended questions are thoughtfully crafted.
- Data Capture: Responses from interviews can be captured digitally, reducing the risk of data loss or errors.
- Transcription: Some software offers automated transcription services, saving time and effort.
- Analysis Tools: Advanced software often includes text analysis tools to identify themes and patterns and keywords in responses.
- Reporting: Researchers can generate reports and visualizations to communicate findings effectively.
By embracing in-depth interview software, researchers can streamline their data collection and analysis processes, allowing for more efficient and insightful research outcomes.
Analyzing Text Messages
Deciphering Digital Dialogues
In today’s interconnected world, text messages have become a ubiquitous form of communication. Analyzing text messages, whether in the context of research, marketing, or customer support, presents a unique opportunity to understand the language and sentiment of individuals.
“Text messaging is a reminder that you’re significant to somebody, or that somebody wants to connect with you, especially if you’re getting a lot of messages from a lot of different people.” — Jim Taylor
Text message analysis involves:
- Sentiment Analysis: Determining the emotional tone of messages, whether positive, negative, or neutral.
- Language Analysis: Examining the language used to identify keywords, trends, and themes.
- Contextual Analysis: Understanding the context of messages, such as the timing and frequency of communication.
- Social Listening: Monitoring social media text to gauge public sentiment and trends.
For instance, a marketing team might analyze customer feedback received through text messages to identify common pain points and areas for improvement in their products or services.
Analyzing Customer Feedback
Enhancing Customer Experiences
Analyzing customer feedback is a cornerstone of modern business strategies. In an era of heightened competition, companies that prioritize customer satisfaction gain a significant edge. Open-ended questions are vital in this context, as they uncover the granular details of customer experiences.
“The key is to set realistic customer expectations and then not to just meet them, but to exceed them.” — Walt Disney
Customer feedback analysis involves:
- Segmentation: Grouping feedback by categories, such as product quality, customer service, or pricing.
- Sentiment Analysis: Assessing the emotional tone of feedback to gauge customer satisfaction.
- Trend Identification: Identifying recurring themes or issues mentioned by customers.
- Actionable Insights: Extracting insights that can lead to concrete improvements in products or services.
By carefully analyzing open-ended feedback, businesses can enhance their offerings, improve customer retention, and ultimately drive growth.
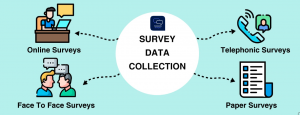
Analyzing Survey Data
Uncovering Nuances in Surveys
Surveys are a common method for collecting data in various fields, from market research to healthcare. While closed-ended questions provide quantitative data, open-ended questions in surveys offer a deeper layer of understanding.
“The real voyage of discovery consists not in seeking new landscapes, but in having new eyes.” — Marcel Proust
Analyzing survey data with open-ended questions involves:
- Thematic Analysis: Identifying recurring themes and patterns in the open-ended responses.
- Comparative Analysis: Comparing open-ended responses with quantitative data to identify correlations or discrepancies.
- Segmentation: Grouping respondents based on their open-ended responses for targeted analysis.
- Contextualization: Understanding how open-ended responses relate to the overall survey objectives.
For instance, in a healthcare survey, open-ended questions can reveal the specific challenges patients face in managing chronic conditions, shedding light on areas where healthcare providers can offer better support.
Analyzing Text Definition
Decoding the Essence of Text
Analyzing text, whether in the form of written narratives, social media posts, or interviews, involves understanding the essence of language. It requires the skills to decipher meanings, context, and underlying emotions within the text.
“Language is the road map of a culture. It tells you where its people come from and where they are going.” — Rita Mae Brown
Text analysis often employs the following techniques:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Utilizing machine learning algorithms to process and understand text data.
- Word Frequency Analysis: Identifying the most frequently used words and phrases to highlight key themes.
- Contextual Analysis: Examining the surrounding context of words to determine their intended meanings.
- Semantic Analysis: Exploring the semantic relationships between words and concepts.
- Sentiment Analysis: Assessing the emotional tone and sentiment conveyed within the text.
By mastering these techniques, analysts can extract valuable insights from textual data, unlocking hidden meanings and patterns that inform decision-making.
In conclusion, qualitative and open-ended questions serve as powerful tools for delving into the depths of human experiences, thoughts, and emotions. Whether applied in research, counseling, or business, they offer a unique lens through which to explore the complexities of our world. As technology continues to advance, the analysis of textual data, including text messages, customer feedback, and survey responses, becomes increasingly vital. By harnessing the potential of open-ended questions and qualitative text analysis, individuals and organizations can uncover the insights needed to thrive in an ever-evolving landscape of information and knowledge.