Embark on a journey through the intricacies of dynamic systems as we delve into the fascinating realm of “Positive and Negative Feedback Examples.” From the finely tuned processes within the human body to the nuanced dynamics of workplace interactions, this exploration unveils the pivotal role played by feedback mechanisms. Discover how positive feedback amplifies outcomes, fostering growth, while negative feedback acts as a corrective force, maintaining equilibrium.
Join us in unraveling real-world instances that showcase the impact and significance of these feedback types as sentiment analysis in various contexts.
What are some negative feedback examples?
Negative sentiment feedback is a crucial component in various systems, providing corrective measures to maintain balance. In the human body, a classic negative feedback example is the regulation of body temperature. When the body overheats, sweat glands are activated to cool down through evaporation, bringing the temperature back to a normal range. Similarly, in business, negative feedback can be constructive criticism that prompts improvements, fostering growth and adaptation.
What is an example of positive and negative feedback in nature?
Nature offers an array of examples illustrating the interplay of positive and negative feedback loops. A notable instance is the predator-prey relationship in ecosystems. When prey populations increase, it provides more food for predators, leading to a surge in predator numbers.
However, as predators thrive, they exert increased pressure on prey, causing a subsequent decline in prey populations—a classic example of negative feedback regulating the system.
What are 3 examples of positive feedback in homeostasis?
Positive feedback amplifies deviations from a set point, often leading to dynamic outcomes. In homeostasis, childbirth serves as a prominent example of positive feedback. The initial contractions during labor stimulate the release of oxytocin, intensifying contractions further. This escalating cycle continues until childbirth is complete, showcasing how positive feedback contributes to the regulation of complex biological processes.
Positive and negative feedback examples in the workplace
Positive feedback in the workplace plays a pivotal role in employee motivation and performance. Recognition for a job well done, promotions, and positive reinforcement contribute to a thriving work environment. Conversely, negative feedback, when delivered constructively, serves as a tool for improvement, guiding employees toward enhanced skills and efficiency.

Positive and negative feedback examples for employees
Positive feedback for employees can encompass acknowledgment of achievements, successful projects, or exemplary teamwork. On the contrary, negative feedback should be framed constructively, addressing areas for improvement rather than demoralizing individuals. Striking a balance between positive and negative feedback fosters a culture of continuous growth and development within an organization.
Difference between positive and negative feedback
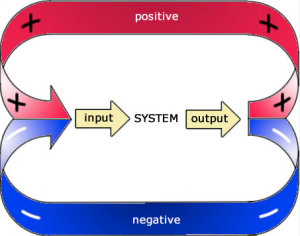
The fundamental distinction lies in their impact on a system. Positive feedback amplifies deviations, potentially leading to significant changes or outcomes. Negative feedback, conversely, works to stabilize and regulate, maintaining equilibrium within a system. Understanding this difference is crucial in navigating feedback dynamics in various contexts.
Examples of positive feedback in the body
Positive feedback in the body is evident in blood clotting. When a vessel is injured, platelets initiate clotting and release chemicals that attract more platelets—a cascading effect that rapidly forms a blood clot to prevent excessive bleeding. This intricate process showcases the significance of positive feedback in responding to critical situations.
Examples of negative feedback in the body
Negative feedback maintains physiological balance, such as the regulation of blood glucose levels. After a meal, blood glucose rises, prompting the pancreas to release insulin. Insulin facilitates the uptake of glucose by cells, lowering blood sugar levels. This exemplifies the corrective nature of negative feedback in sustaining homeostasis.
In conclusion, classifying positive and negative feedback examples is pivotal in comprehending the intricacies of dynamic systems, whether in nature, the workplace, or the human body. Both forms of feedback contribute uniquely to stability, adaptation, and growth, emphasizing their indispensable roles in diverse aspects of our lives.
As Winston Churchill aptly said, “Criticism may not be agreeable, but it is necessary.
It fulfills the same function as pain in the human body. It calls attention to an unhealthy state of things.” In essence, feedback—whether positive or negative—serves as a catalyst for improvement and evolution, propelling us toward greater heights.